pool chemical chart pdf
Pool Chemical Charts⁚ A Comprehensive Guide
This guide provides essential information on understanding and utilizing pool chemical charts. It covers interpreting dosage charts, calculating chemical needs for various pool sizes, and adjusting levels based on test results. Accurate chemical balance ensures bather safety and optimal water clarity, minimizing maintenance and maximizing enjoyment. Learn how to maintain proper pool chemistry with easy-to-understand charts and advice.
Understanding Pool Water Chemistry Basics
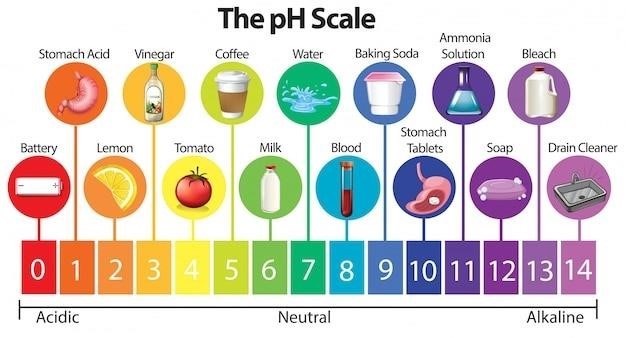
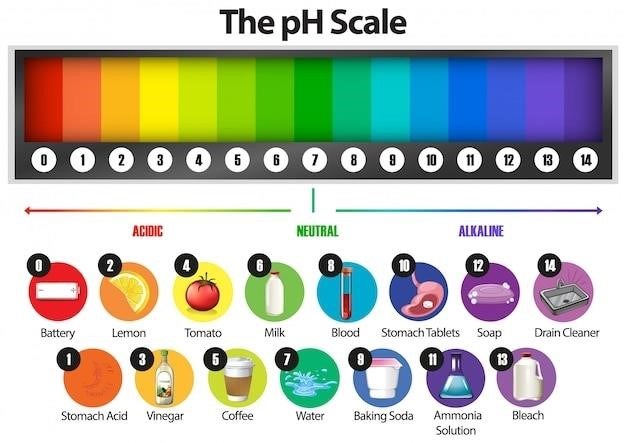
Maintaining a healthy swimming pool involves understanding fundamental water chemistry. Key parameters include pH, alkalinity, and sanitizer levels (like chlorine). pH measures acidity or alkalinity, ideally ranging from 7.2 to 7.8. Alkalinity buffers pH changes, preventing drastic fluctuations. Sanitizer levels, typically chlorine, eliminate bacteria and algae, requiring regular monitoring and adjustments. Inadequate levels lead to cloudy water or algae blooms. Testing kits provide accurate measurements. Understanding these basics is crucial for effective pool maintenance and avoiding costly problems. Proper balance prevents corrosion of pool equipment and ensures a safe and enjoyable swimming experience. Regular testing and adjustments, guided by a pool chemical chart, are key to success. Ignoring these basics can lead to health risks and expensive repairs. Therefore, learning and applying this knowledge is fundamental to responsible pool ownership.
Ideal Chemical Levels for Different Pool Types
Optimal chemical levels vary depending on your pool type. In-ground pools, with their larger volume and exposure to sunlight, often require slightly different chemical balances than above-ground pools. For instance, chlorine levels might need to be higher in larger, sun-exposed pools to combat algae growth. Similarly, pH and alkalinity targets may differ based on factors such as the pool’s material (concrete, vinyl, fiberglass), climate, and bather load. Spas, with their higher water temperatures and more concentrated use, demand more frequent monitoring and adjustments, often requiring higher sanitizer levels. A dedicated spa chemical chart should be consulted. Always refer to a comprehensive pool chemical chart that specifically addresses the type of pool you own, factoring in regional climate conditions and usage patterns. Regular testing and adjustments, following the guidelines for your specific pool type, ensure a clean, safe, and enjoyable aquatic environment.
Common Pool Chemicals and Their Functions
Maintaining a healthy swimming pool involves understanding the roles of various chemicals. Chlorine, the most common sanitizer, kills bacteria and algae. Insufficient chlorine leads to cloudy water and potential health risks. Maintaining the correct pH level (7.2-7.8) is crucial; imbalances can corrode pool surfaces or irritate swimmers’ skin and eyes. Alkalinity buffers pH fluctuations, preventing drastic changes. Calcium hardness prevents scaling and corrosion. Cyanuric acid, or stabilizer, protects chlorine from degradation by UV sunlight. Algaecides prevent algae growth, even when chlorine levels are adequate. Clarifiers improve water clarity by clumping small particles together for easier filtration. Shock treatments, usually containing chlorine or non-chlorine oxidizers, rapidly eliminate contaminants and restore water clarity. Understanding these chemical functions empowers you to effectively maintain your pool’s health and cleanliness.

Using Pool Chemical Charts Effectively
Pool chemical charts simplify water treatment. They provide clear guidelines for determining the correct amount of each chemical needed based on your pool’s size and water test results. Accurate readings ensure safe and enjoyable swimming.
Interpreting Chemical Dosage Charts
Understanding pool chemical dosage charts is crucial for maintaining balanced water chemistry. These charts typically list various water parameters (pH, alkalinity, chlorine, etc.) along with recommended ranges for optimal pool health. They usually present the information in a tabular format. Each row represents a specific parameter, indicating the ideal level and potential consequences of imbalances. The charts often include columns showing the appropriate chemical to use for adjustment and the recommended dosage for different pool volumes. Look for charts that clearly specify units of measurement (e.g., parts per million or milligrams per liter) to avoid confusion and ensure accurate calculations. Pay close attention to the instructions provided with the chart, as different charts may use different scales or units of measurement. Always double-check your calculations before adding any chemicals to your pool. Remember, adding too much of any chemical can be harmful to swimmers and damage pool equipment; Proper interpretation of chemical dosage charts will lead to successful pool maintenance and a safer, more enjoyable swimming experience.
Calculating Chemical Requirements for Your Pool
Accurately calculating chemical needs is essential for maintaining a healthy and balanced pool; Begin by determining your pool’s volume. This can be done using online calculators readily available, requiring only the pool’s dimensions as input. Once the volume is known, consult a reliable pool chemical chart. These charts typically provide recommended chemical levels for various parameters, such as pH, alkalinity, and sanitizer (chlorine). The chart will often present these recommendations in units such as parts per million (ppm) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). Next, compare your test results (obtained using a reliable testing kit) with the ideal ranges indicated on the chart. If your levels are outside the recommended ranges, the chart will usually guide you on the necessary adjustments. Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions on the chemical packaging. Using the pool volume and the recommended dosage per unit volume provided in the chart, you can calculate the required amount of each chemical needed for correction. Always add chemicals slowly and carefully, while constantly monitoring the water with a testing kit. Avoid adding too much at once and always ensure thorough mixing after adding any chemicals.
Adjusting Chemical Levels Based on Test Results
Regular water testing is crucial for maintaining optimal pool chemistry. After testing your pool water using a reliable test kit, compare your results to the ideal ranges provided on a pool chemical chart; This chart will indicate the desired levels for pH, alkalinity, calcium hardness, and sanitizer (e.g., chlorine). Discrepancies between your test results and the ideal ranges necessitate adjustments. For instance, if your pH is too low (acidic), you’ll need to add a pH increaser following the instructions on the product label and the dosage recommendations on your chosen chart. Conversely, if the pH is too high (alkaline), a pH decreaser is required. Similarly, low sanitizer levels indicate a need for additional chlorine or other sanitizing agents. Always add chemicals slowly and carefully, following the manufacturer’s instructions precisely. After adding chemicals, allow sufficient time for thorough mixing before retesting. Remember that significant adjustments might require multiple smaller additions, followed by retesting, to avoid drastic imbalances. Consistent monitoring and small, incremental adjustments, guided by your pool chemical chart, will ensure a safe and enjoyable swimming experience.
Maintaining Proper Pool Chemistry
Consistent monitoring and adjustments, guided by a reliable pool chemical chart, are key to maintaining balanced water chemistry. This ensures a safe, comfortable, and enjoyable swimming experience while minimizing maintenance issues.
Regular Water Testing and Monitoring
Regular water testing is paramount for maintaining a healthy and safe swimming pool. Employing test strips or a liquid test kit, check pH, alkalinity, and sanitizer levels weekly. These parameters are crucial for preventing algae growth, bacterial contamination, and equipment corrosion. Accurate readings, facilitated by a clear understanding of your pool’s chemical chart, allow for precise chemical adjustments. This proactive approach prevents imbalances from escalating into costly and time-consuming problems. Remember, neglecting regular testing can lead to cloudy water, unpleasant odors, and potential health risks for swimmers. The frequency of testing might need to be increased during periods of heavy use or extreme weather conditions. Consistent monitoring ensures your pool remains a clean and enjoyable oasis, maximizing your investment and minimizing potential issues.
Preventing and Addressing Common Water Problems
Proactive pool maintenance, guided by a comprehensive understanding of pool chemical charts, is key to preventing common water issues. Cloudy water often indicates an imbalance in pH, alkalinity, or sanitizer levels. Algae blooms, typically appearing as green or brown discoloration, signify insufficient sanitizer. Scale buildup on pool surfaces suggests high calcium hardness. By regularly testing and adjusting chemical levels according to your pool’s specific needs, you can prevent these problems before they arise. Should issues occur, consult your chemical chart to identify the imbalance and make appropriate corrections. Remember to always add chemicals slowly and carefully, following instructions precisely. For persistent problems, consider seeking professional assistance from a pool service technician who can accurately diagnose and resolve complex chemical imbalances. Preventative measures are far more economical and efficient than reactive treatments.
Ensuring Bather Safety and Comfort
Proper pool water chemistry, as detailed in pool chemical charts, is paramount for bather safety and comfort. Maintaining the correct pH level (7.2-7.8) prevents skin and eye irritation, ensuring a pleasant swimming experience. Inadequate sanitizer levels, such as chlorine, can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria and pathogens, posing health risks. Conversely, excessively high sanitizer levels can also cause irritation. Regular testing and adjustments, guided by the chart, are essential. Total alkalinity should be within the recommended range to prevent corrosion of pool equipment and maintain stable pH. Calcium hardness should also be balanced to avoid scaling. Always follow the instructions on chemical packaging and prioritize safety. For those with sensitive skin, consider using gentler sanitizing methods or alternative pool treatments. Prioritizing proper water chemistry ensures a safe and enjoyable swimming environment for all bathers.